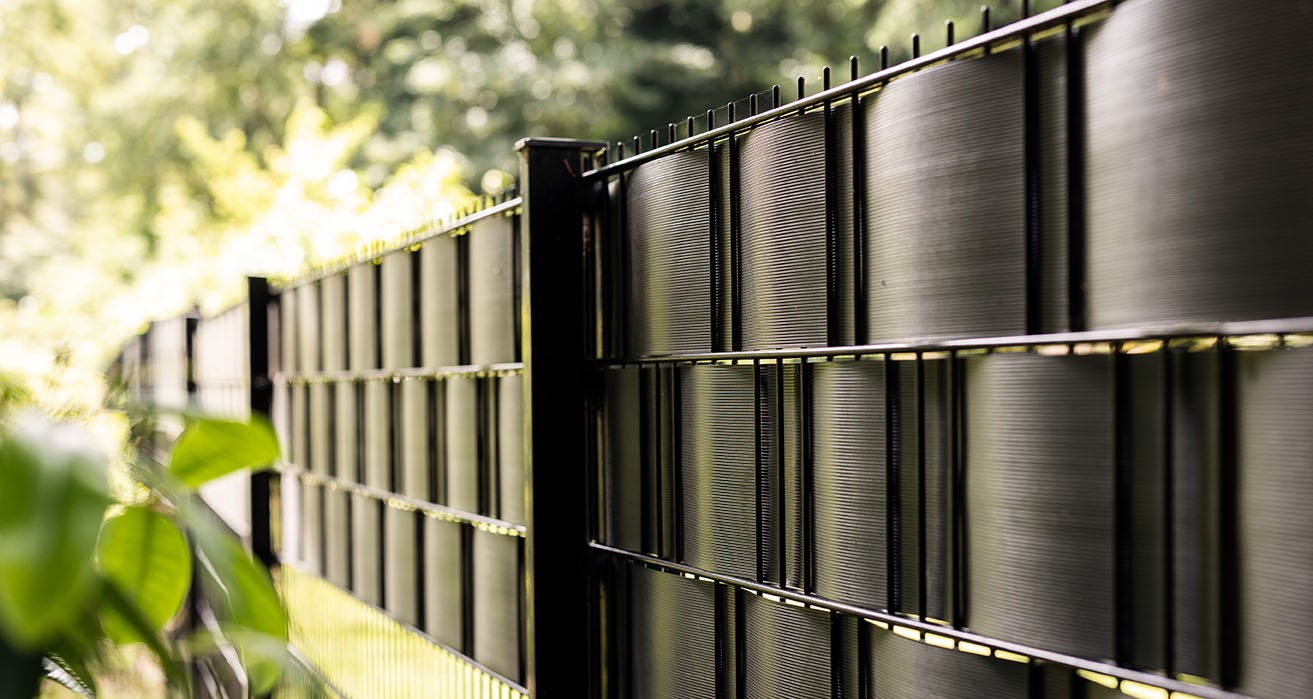
Fencing has played a critical role in human civilization for centuries. Beyond its basic function as a physical barrier, fencing has served as a symbol of authority, a means of protection, and a key element in urban and industrial development. Understanding the history of fencing provides valuable insights into its modern applications in commercial and industrial settings. Here are seven key facts about the evolution of fencing that every business should know.
1. Ancient foundations
Fencing dates back to ancient civilizations, including the Egyptians and Romans, who used wooden and stone barriers to define property boundaries and protect valuable assets. Early fences were also used strategically to keep livestock secure and deter external threats. The fortified walls of Rome exemplify how fencing was historically employed for large-scale security and defense.
2. Status and prestige in the middle ages
During the Middle Ages, fences were not only functional but also symbols of wealth and status. Aristocratic families and royal estates showcased ornate iron fencing, often adorned with elaborate patterns and family crests. These decorative elements reinforced the prestige and authority of property owners, a trend that continues today in high-end residential and commercial properties.
3. The industrial revolution and the rise of wrought iron
The 18th and 19th centuries saw the widespread adoption of wrought iron fencing, thanks to advances in industrial manufacturing. The increased availability of wrought iron made it a preferred choice for both residential and commercial applications, particularly in urban environments like London and New York. Its combination of durability and aesthetic appeal made it a staple in city planning and property management.
4. Modern functional fencing
The 20th century ushered in a shift toward more functional fencing solutions, driven by the development of new materials such as steel and aluminum. These materials offered enhanced strength and longevity, making them ideal for industrial, commercial, and institutional use. Today, fencing solutions prioritize security and efficiency, with applications ranging from warehouse perimeters to corporate office spaces.
5. Technological advancements in security fencing
The 21st century has introduced smart fencing solutions that integrate cutting-edge technology. Businesses now have access to security-enhancing features such as automated gates, motion sensors, and surveillance integration. Smart fencing is particularly valuable in industries requiring high-security measures, such as logistics, data centers, and government facilities. These innovations provide real-time monitoring and remote access, significantly improving security management.
6. Sustainability in fencing materials
As sustainability becomes a core business priority, companies are increasingly opting for eco-friendly fencing solutions. Materials such as bamboo, recycled plastic, and composite alternatives offer long-term durability while reducing environmental impact. Sustainable fencing is particularly relevant for businesses looking to align with green building initiatives and corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals.
7. Enhancing community and workplace safety
Fencing plays a vital role in ensuring safety within both public and private spaces. From securing corporate campuses to safeguarding public parks and schools, strategic fencing solutions help mitigate security risks and enhance controlled access. For businesses, implementing well-designed fencing can contribute to employee safety, asset protection, and regulatory compliance.
For the latest trends and expert insights into fencing solutions for your business, visit Fenceweb.com. Whether you need security enhancements, sustainable options, or modern fencing technology, Fenceweb.com provides comprehensive resources to help you make informed decisions.
This article offers a professional overview of fencing’s historical evolution and its relevance to modern business applications. By understanding the significance of fencing innovations, organizations can optimize security, efficiency, and sustainability in their operations.