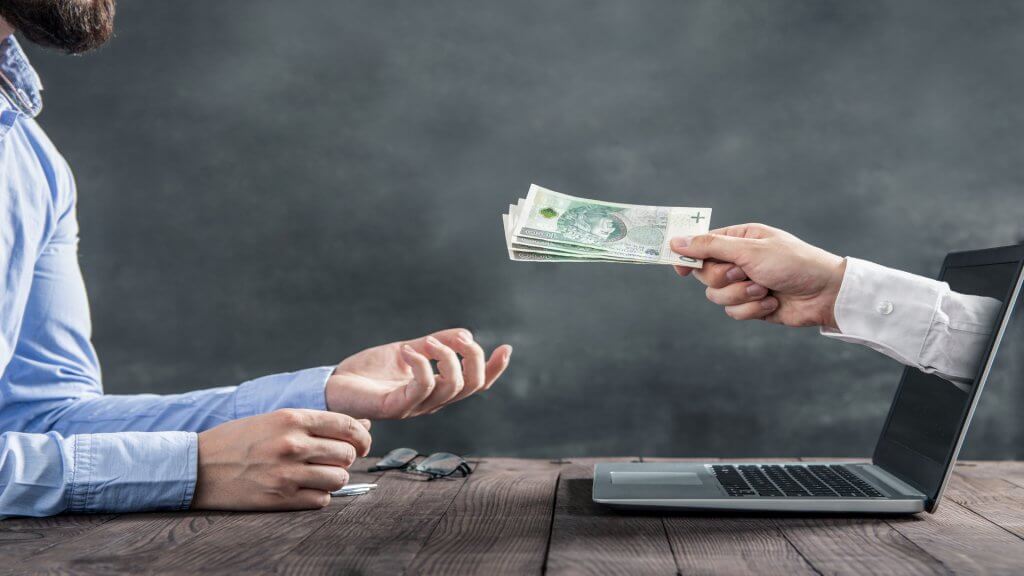
Money transfers have become a routine part of our daily lives. However, as their popularity has grown, so have fraudulent schemes—money theft can happen within minutes. To protect yourself from scams, it is crucial to be aware of potential risks and understand how to avoid them. In this article, we will not only explore common fraud tactics but also discuss secure ways to protect your financial transactions.
Common Fraud Schemes
Money transfer scams occur when fraudsters impersonate trusted individuals (employees of official organizations, colleagues, acquaintances, or relatives) and trick people into sending money through an online service. Since these transactions happen almost instantly, they are often difficult to cancel. Victims have very little time to realize the mistake, react, and attempt to reverse the transaction. This is why transfer fraud is widespread and highly effective.
Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common scams.
Extortion and Blackmail
Scammers may demand money, valuables, or assets by using threats and intimidation. One example is sextortion, where criminals threaten to reveal compromising information, such as explicit photos or videos, unless the victim complies with their demands—usually financial.
Impersonating Officials
Fraudsters pose as bank employees or representatives of other institutions, claiming:
- Erroneous payments or bank transfers that must be refunded
- Delivery issues or fake fees requiring immediate payment
They pretend to be solving an issue but are actually trying to obtain personal or financial information to carry out unauthorized transactions.
Fake Tech Support
Scammers pose as representatives of major companies (e.g., Microsoft, Apple) and claim that the victim’s computer has serious issues that require immediate action. They contact victims via phone, email, or pop-up messages, impersonating tech support. Their goal is to gain remote access to the victim’s computer to steal money or personal data.
Immigrant Scams
A scammer impersonates an immigration official, claiming there are problems with the victim’s documents. They insist that the issue can only be resolved by sending money urgently or providing bank account details. These fraudsters may mention personal details to sound convincing and even threaten deportation. In such cases, it is best to hang up immediately and contact the relevant government agency using official contact information.
Fake Lottery and Prize Scams
These scams involve phony lotteries and sweepstakes. Victims receive an unexpected call or email informing them of a huge prize. The fraudsters then request bank account details to “transfer the winnings”, but instead, they steal the victim’s money. Another version involves scammers sending a fake check and asking the victim to pay a fee to cover “processing costs”. Once the victim cashes the check and sends the money, the check bounces, leaving them with a financial loss and potential bank penalties.
Bank Card Data Theft
A scammer contacts a victim, pretending to be a buyer interested in purchasing an item. After discussing pricing and details, they offer to pay via money transfer. Then, they send a fraudulent link to a fake payment page that asks for the seller’s full bank card details under the pretense of “confirming the transfer.” Once the victim enters the information, their card is charged, and the fraudster disappears.
How to Avoid Falling Victim to Scammers
To protect your funds, it is essential to follow a few simple rules:
- Be cautious when receiving unexpected messages. Scammers often disguise themselves as bank representatives or officials, sending fake emails or messages asking for urgent money transfers or personal information. Always verify such requests by contacting the organization directly through official channels.
- Use only licensed and reputable money transfer services. Before choosing a transfer method, research reviews and ensure the service is reliable.
- Don’t trust offers that seem too good to be true. If someone offers you high-return financial opportunities or asks for money to claim a prize, be skeptical—these are common fraud tactics.
- Protect your personal data. Never share banking details, passwords, or PIN codes with strangers. Scammers often use this information to access and steal your money.
How to Choose a Money Transfer Method
Choosing a secure money transfer method is key to protecting your funds. Let’s explore the main options available.
Bank Transfers
Bank transfers are considered one of the most reliable ways to send money. Banks provide a high level of transaction security and offer various services, including international transfers, which allow you to send money directly to the recipient’s bank account in another country. However, you should consider the processing time and possible fees associated with these transfers.
Specialized Money Transfer Services
Due to their convenience and speed, specialized money transfer services are gaining popularity. Platforms such as KoronaPay Europe, TransferGo, Wise, and Remitly allow users to send money online, bypassing traditional banking procedures. These services offer competitive fees and almost instant processing times, even for international transactions.
For example, Wise allows money transfers to all Eurozone countries, the U.S., and more. KoronaPay Europe specializes in money transfers from Europe to the Commonwealth of Independent States – CIS countries. PayPal operates in 200 countries and supports 24 currencies. Remitly is continuously expanding its list of supported countries, including smaller island nations.
Using Cryptocurrencies
For some users, cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum are an attractive alternative for sending money abroad. However, when choosing this option, consider that:
- Cryptocurrency prices fluctuate significantly.
- Some countries have restricted or banned their use.
- A good understanding of blockchain technology and digital asset storage is required for safe transactions.
Regardless of the chosen method for making transfers, it is important to follow these simple security rules:
- Double-check recipient details. Always carefully verify the recipient’s information before sending funds.
- Use two-factor authentication. Enable an additional layer of protection for access to your financial accounts.
- Update software. Regularly update the apps and systems you use for transactions to protect against vulnerabilities.
- Avoid public Wi-Fi networks. It is not recommended to perform financial transactions over unsecured or public networks.
By following these recommendations, you can minimize risks and secure your transfers.